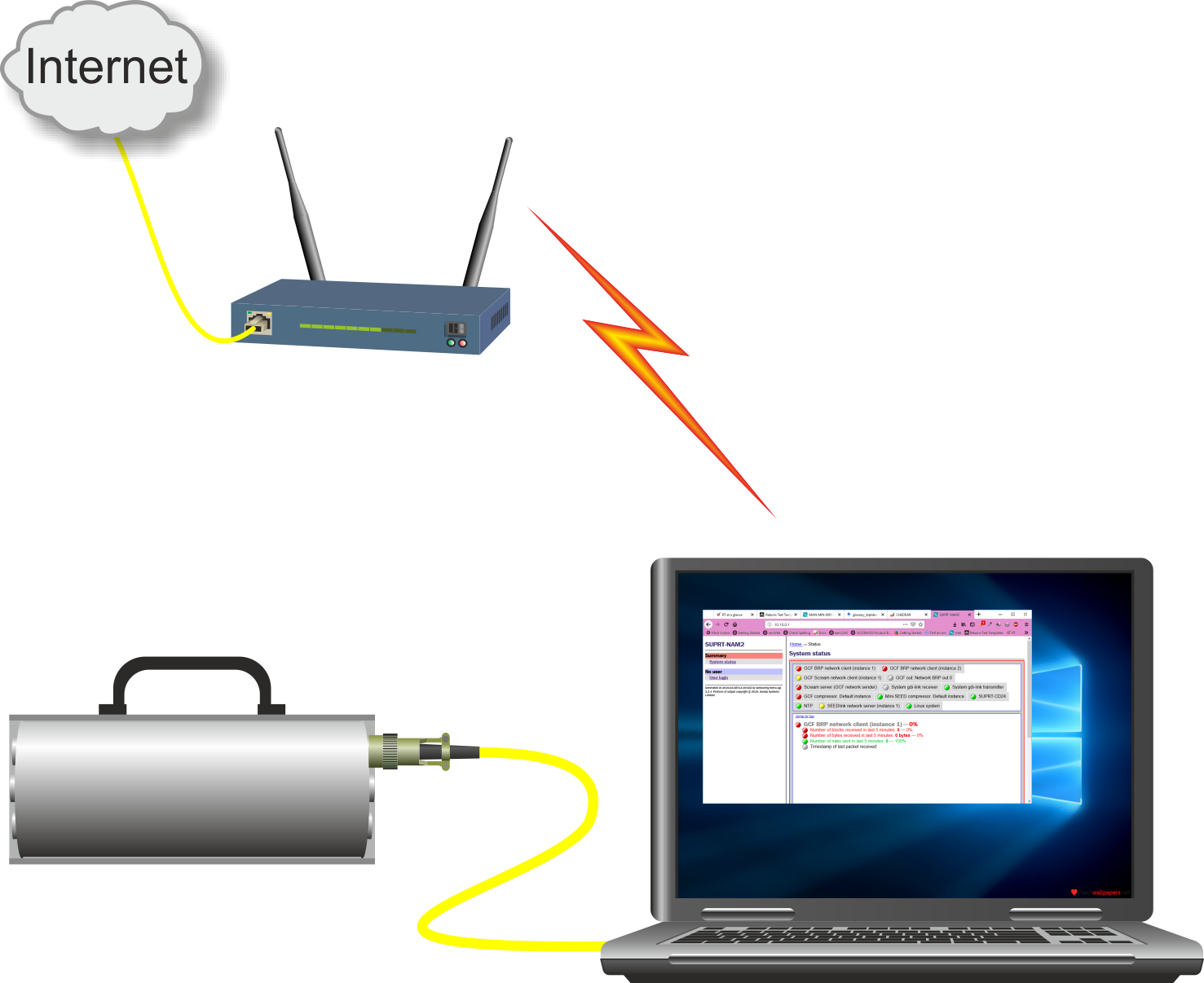
It is sometimes awkward to connect a Platinum systemA "Platinum system" is any system running the Platinum operating system. This includes stand-alone acquisition systems such as EAMs and NAMs, DAS units such as the Affinity and DM24SxEAM and digital instruments with built-in acquisition systems such as the 3TDE, 40TDE or 5TDE., such as an EAM or 40TDE instrument, to the Internet for firmware upgrades. For example: in some cases, the only available Internet access is via WiFi so, if the Platinum system does not have a WiFi interface, direct connection becomes impossible. In these cases, a PC or laptop can be used as a gateway, allowing the Platinum system to contact the Güralp firmware server indirectly, via the PC.
Another example where this technique is useful is when a remote Platinum system is connected to a data-centre via a VPNVPN stands for Virtual Private Network which is a technique for passing data across the public Internet as if it were a dedicated, private network link. See Wikipedia's VPN page for more information.; In this case, a PC at the data-centre which has both VPN and Internet access can be used as a firmware-upgrade gateway.
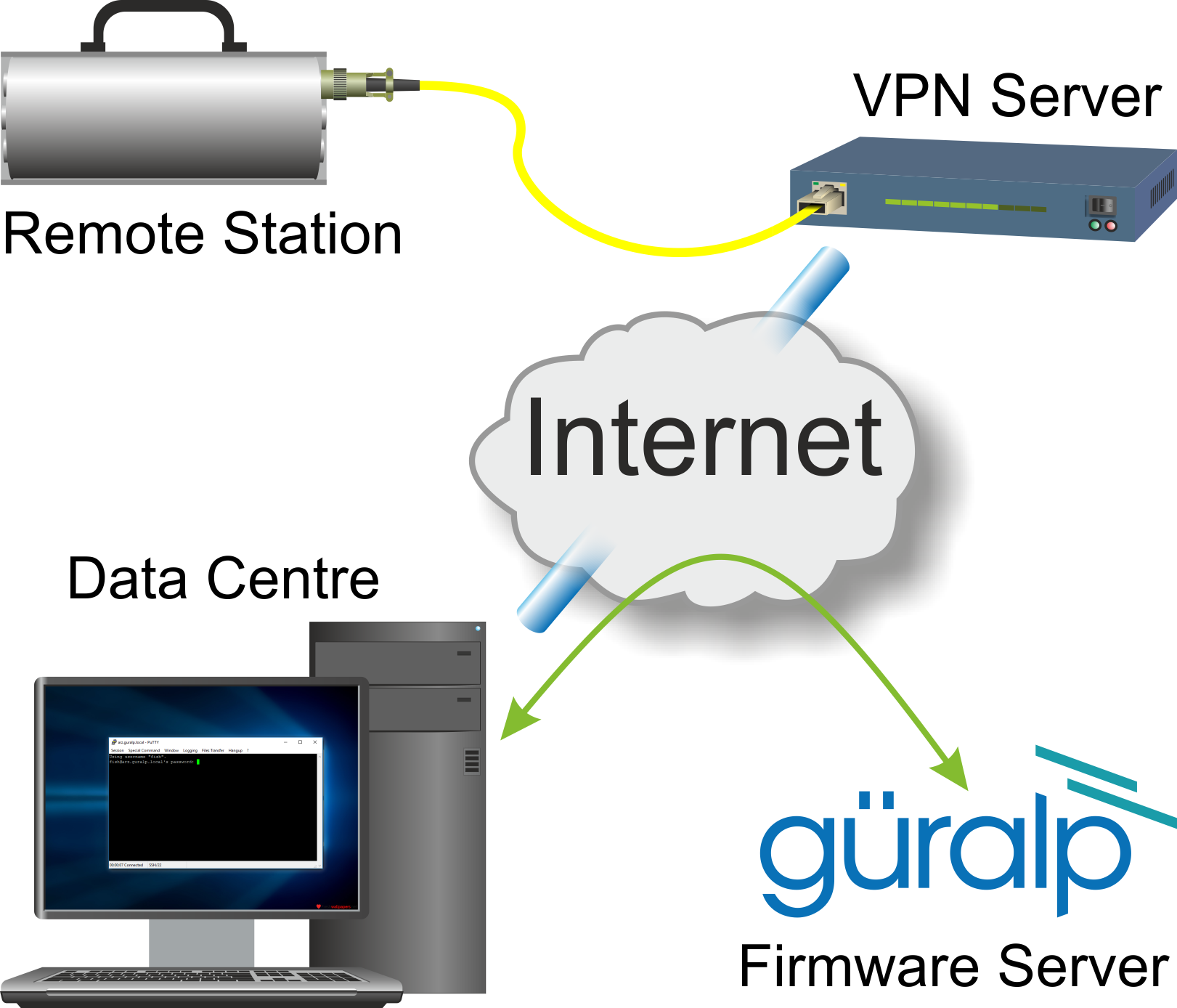
This article describes one way to set up a PC for this purpose. For windows users, we will use the (free) PuTTY terminal emulation software to make a local network connection to the Platinum system while providing a port-forwarding facility which the Platinum system can use to contact the firmwqare upgrade server. Linux users can do the same or use a much simpler command-line technique.
The PC is configured to make an SSH Secure SHell is a command (and associated protocol) which creates an authenticated and encrypted channel between two systems on a network. It can be used to run commands on a remote system, amongst other uses. See Wikipedia's SSH page for more information. connection (shown as a blue arrowed line below) to the Platinum system. This connection is configured with a port-forwarding rule which causes the ssh server on the Platinum system to listen for incoming connections on TCP port 8730. If it receives any such connections, it will transparently forward them, via the PC, to port 873 on the firmware upgrade server, as shown by the dotted purple line.
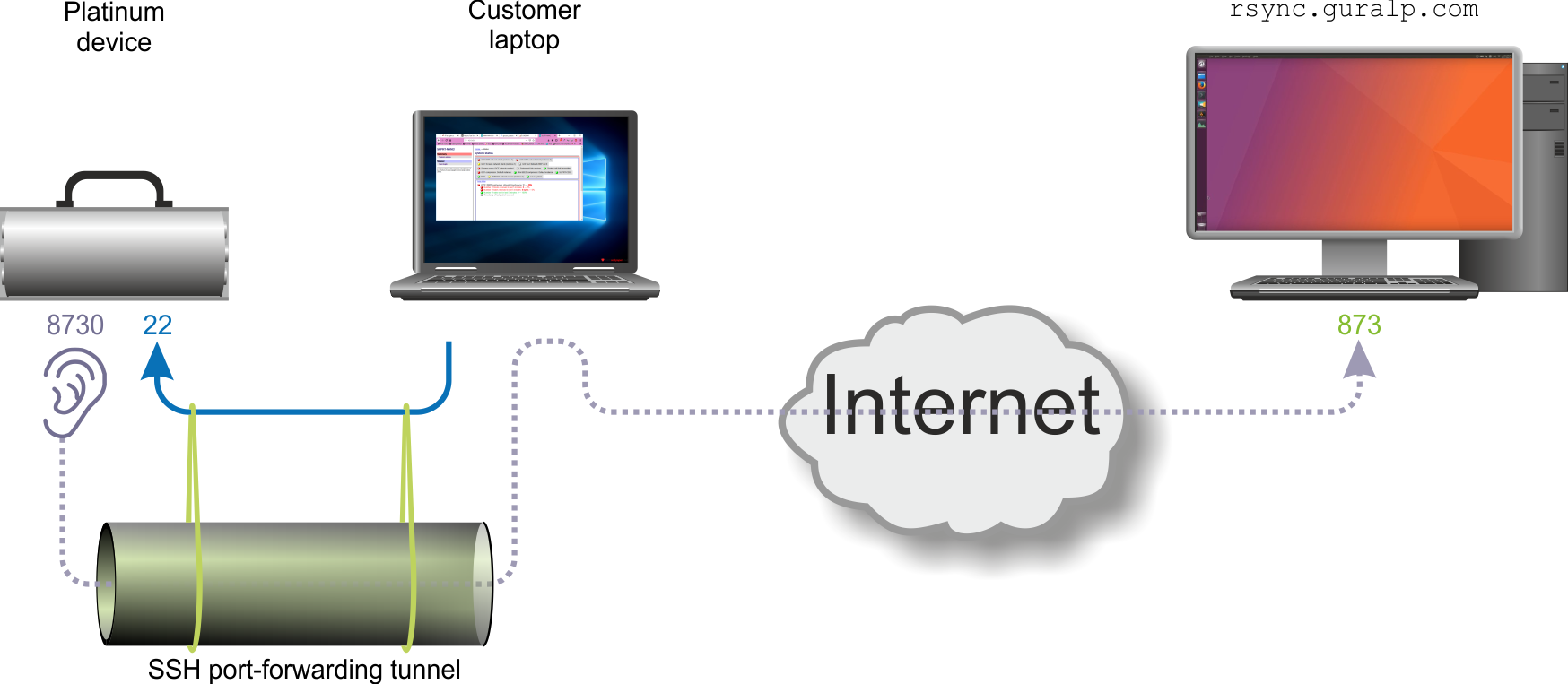
Next, the firmware upgrade system on the Platinum device has to be reconfigured. Instead of connecting directly to the firmware upgrade server, we'll set it to connect to port 8730 on its own loopback address A loopback address is any address in the range 127.0.0.1 to 127.255.255.255 but, typically, 127.0.0.1 is used. Such addresses are treated as special by the operating system's network software and connections made to these addresses are connected directly back to the originating system, without ever appearing on the network cable. Instead, an internal, software-based virtual network adapter, the loopback adapter is used. For more information, see Wikipedia's "Localhost" page.. This connection is transparently forwarded (by PuTTY or ssh on the PC) to the real firmware upgrade server.
At this point, the firmware upgrade system on the Platinum device can be initiated as usual. The connection to the firmware upgrade server is made through an SSH tunnel, so it is protected by strong encryption.
The instructions differ depending on whether you run Windows or Linux on the PC that you intend to use for the gateway machine. Choose one of the following links for instructions relevant to your operating system.